|
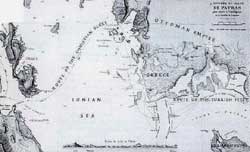
N a f p a k t o s the Jewel of the Corinthian Gulf , where the famous
Naval Battle of Lepanto took place on Oct 7 , 1571 .The Gulf of Lepanto
is a long arm of the Ionian Sea running from east to west and separating
the Pelloponnesian peninsula to the south from the Greek mainland to the
north.
Jutting headlands divide the Gulf into two portions: the inner one,
called the Gulf of Corinth today , ends with the isthmus of the same
name , and the outer one is an irregular , funnel-shaped inlet now
called the Gulf of Patras. For six weeks Ali Pasha's ships had been
anchored inside the fortified harbor of Lepanto located in the
gulf's inner portion, and on October 5 they began to move slowly
westward past the dividing headlands into the outer Gulf of Patras.
Still unsure of the enemy's position , Ali Pasha ordered his fleet
to drop anchor for the night in a sheltered bay fifteen miles from
the entrance to the inlet, where it remained all the next day
anxiously awaiting the return of the scouting vessels. |
|
|
Click on Picture to Enlarge |
Around midnight Kara Kosh reached the anchorage with the news that
the Christian fleet was then at Cephalonia , an Ionian island almost
directly opposite and parallel to the mouth of the Gulf of Lepanto. With
the first light of dawn the following morning , October 7 , 1571 ,
lookouts stationed high on a peak guarding the northern shore of the
gulf's entrance signaled to Kara Kosh that the enemy was heading south
along the coast and would soon round the headland into the gulf itself.
The signal was relayed to Ali Pasha , who gave the order to weigh
anchor. Everyone scrambled to battle stations and , as the fleet
advanced , strained for the first sight of the enemy force. |
|
The Christian fleet had started to move southward toward the Gulf of
Lepanto. Now only fiteen miles of open water separated the forces of
Islam and those of Christendom. The Turkish fleet , which numbered over
two hundred and thirty galleys and one hundred auxiliary vessels , Ali
Pasha commanded the center squadron , which faced the one commanded by
Don Juan of Austria. |
|
According to naval practice in those days , the moment two rival fleets
finally assumed their respective battle formations , the leader of one
would fire a piece of artillery as a challenge to fight , and the
opponent would answer by firing two cannon to signify that he was ready
to give battle. This day it was the Turks who made the challenge , and
the sharp report from Ali Pasha's flagship was quickly followed by
double round from Don Juan's artillery. At this time a large green silk
banner , decorated with the Moslem crescent and holy inscriptions in
Arabic , was hoisted on the Turkish flagship.
Now the setting was complete. The cross and the crescent fluttered
aloft , symbolizing the two religions and the two hostile
Civilizations of Christendom and Islam , whose forces were about to
meet in the decisive battle of their long and bitter holy war. |
Click on Picture to Enlarge |
|
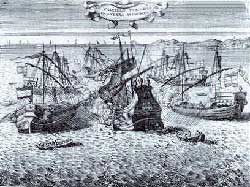
With the very first barrage
many Turkish galleys were sunk and over a score badly damaged. After an
hour of heavy fighting it was captured , the first Christian prize of
the battle. The Christians were more than a match for them. In fact ,
they fought with such incredible ferocity that the battle soon became a
slaughter. The defeat of the Turk's right wing was complete. Not one
galley escaped. Those that were not sunk , burned , or grounded ashore
were captured by their Christian opponents. The whole battle was over by
four o'clock that afternoon , even though many of the Christian galleys
were still giving chase to the Turkish ships and other solitary escaping
Turkish vessels. The waters of the gulf for miles around were stained
red from the great amount of blood shed that day and the sea was strewn
with the bodies of both victors and vanquished. At sunset there were
signs of approaching bad weather , Don Juan ordered the fleet to regroup
quickly and head for a sheltered bay near the northwestern limits of the
gulf. Around midnight they anchored in the bay and immediately all the
fleet's leaders , with the exception of those badly wounded , came on
board. |
|

Click on Picture to Enlarge |
Don Juan's galley gatherd to congratulate him
and celebrate the victory. The losses suffered by the Holy League
fleet were between seven and eight thousand killed and about twice
that number wounded , and only ten or fifteen ships had been sunk
during the battle. These losses were comparatively light. Of the
three hundred and thirty Turkish ships , fewer than fifty managed to
escape and most of them were burned because they could not be made
sufficiently seaworthy for further use; one hundred and seventeen
Moslem galleys were captured intact and the rest were sunk or
destroyed after they had been run ashore by the fleeing Turks. |
|
A large majority of the seventy-five thousand
men who had entered the battle on the Moslem side were killed , five
thousand were taken prisoner (with at least teice that number of Christian galley slaves
liberated) , and only a few were able to escape either by ship or by
swimming ashore.Turkey, for the first time in several centuries , was
left without a navy.
Word of the fleet's splendid victory at Lepanto preceded Don Juan's
return and quickly spread throughout Europe. The Republic of Venice was
the first allied state to receive the happy news. The Doge quickly
ordered a week of public celebrations and the seventh of October was
declared a perpetual holiday in memory of the Battle of Lepanto.
Hundreds of poems , songs , and paintings were produced all over
Christendom in commemoration of the victory. All of Christendom took
heart. |
|
The famous Spanish writer , Miguel de Cervantes , who himself was
wounded in the Battle of Lepanto , serving in the Spanish infantry , and
who had also been a captive of the Barbary pirates until ransomed ,
recounted many of his experiences in the novel Don Quixote. The Battle
of Lepanto marked the end of Turkish naval supremacy and the beginning
of the Ottoman Empire's decline on both land and sea. Perhaps the most
important result of the battle was its effect on men's minds: the
victory had ended the myth that the Turks could not be beaten.
The Turkish fleet had 208 Galleys, 66 small ships; The Christian
fleet about the same number. |

Click on Picture to Enlarge |
|
The crusaders lost 17 ships and 7,500 men; 15
Turkish ships were sunk and 177 taken, from 20,000 to 30,000 men
disabled , and from 12,000 to 15,000 Christian rowers, slaves on the
Turkish Gaileys, were delivered. Though this Victory did not
accomplish all that was hoped for, since the Turks appeared the very
next year with a fleet of 250 ships before Modon and Cape Matapan,
and in vain offered battle to the Christians, it was of great
importance as being the first great defeat of the infidels on the
sea.
Held by the Venetians from 1687 to 1689, and thence by the Turks
until 1827, it became in the latter year part of the new Greek
realm. Today Nafpaktos (Naupactus,) chief town of the district in
the province of Arcarnania Aetolia, has (12,000 inhabitants), all
Orthodox Greeks.
By
Georgios Rigas |
|
|
|